VIDEO Startup Stock Options: Negotiate the Right Startup Stock Option Offer
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Negotiation Rhythms #3: Sales & Threats
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Mary Russell counsels individual employees and founders to negotiate, maximize and monetize their stock options and other startup stock. She is an attorney and the founder of Stock Option Counsel. You are welcome to contact Stock Option Counsel at info@stockoptioncounsel or (650) 326-3412.
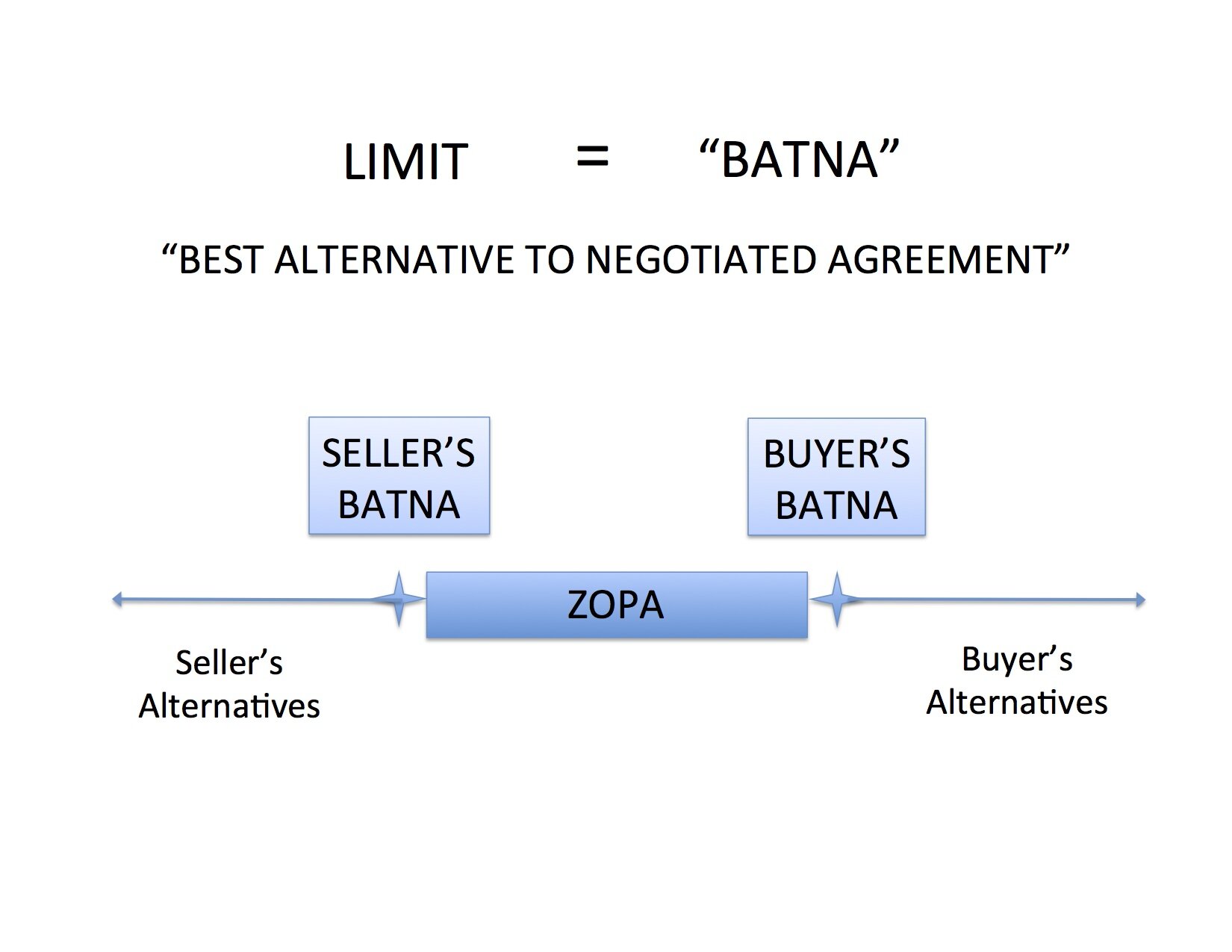
There are two ways to increase or decrease another party’s limit in a negotiation – sales and threats.[1] The picture above takes some of the mystery out of the salesman and the thug -- they're both just working as negotiators to change the perception of the current offer in comparison to the other party's BATNA – Best Alternative to Negotiated Agreement.
Selling improves the perception of the quality of the present offer so that the outside alternatives are unattractive by comparison. Threats decrease the attractiveness of outside offers or the possibility of making no deal and sticking with the status quo.
Threats
An ongoing employment lawsuit over no-hire agreements among Silicon Valley companies featuring Steve Jobs provides a strangely relevant example of the power of threats.
Edward Colligan, former CEO of Palm, has said in a statement that Jobs was concerned about Palm’s hiring of Apple employees and that Jobs “proposed an arrangement between Palm and Apple“ [2] to prohibit either party from recruiting the others' employees.
That would have been a simple offer of an agreement (however illegal that arrangement might have been) if Colligan had access to the undisturbed alternative of not participating and keeping the status quo.
But Colligan has said that Jobs’ next negotiation move was to make the alternative of nonparticipation very unappealing with the threat of patent lawsuits that would cost Palm and Apple a great deal of money. Jobs followed this threat with a reminder of just how unpleasant such litigation would be for Palm, considering the fact that Apple had vast resources to endlessly pursue the lawsuits: "I’m sure you realize the asymmetry in the financial resources of our respective companies …."
Even though most of us don’t use threats in a negotiation, it’s part of the logic of negotiation rhythms.
Selling
Selling is the more common (and generally legal) way to address the fact that the other party has choices outside the present negotiation. As we discussed in the prior posts, a party's price or terms limits are defined by his or her best alternative outside of making an agreement in the present negotiation. Selling moves the limit when it can make the present offer more appealing than what had been perceived as an outside alternative.
Many people resist “selling themselves” in a salary negotiation because they are embarrassed to discuss their “value.” The logic of BATNA and negotiations provides some relief from this embarrassment, for it reframes “selling” from bluffing and puffing to describing and distinguishing one’s past experience and intended role in the organization.
Since the employer’s limit is not defined by an individual’s value, but by the employee’s differentiation from the field of candidates, the task of negotiating becomes more fact-based and less fear-driven. This logic encourages progress from the attitude of “Oh, they see who I am and hate me,” toward the sales approach of “Oh, it seems they need more information about what I offer in terms of my past experience and my role going forward.”
As an employee’s offer of services becomes distinguishable from the employer’s alternatives, the employer’s perception of the BATNA will change.
Consider an employer who believes there’s an equal candidate available for $120,000 and is entertaining another’s proposal to perform the role for $140,000. Without “selling” the offer of one’s services, the employer has no information with which to make a distinction between the two alternatives. The process of selling oneself to the employer is not to prove one’s inner worthiness at $140,000, but to show and tell that the employer is choosing between two distinguishable candidates.
(For those still interested in threats, distinguishing one’s skills is a form of a threat when it comes to negotiating with a current employer. Every element of the description one’s current performance and ongoing role is a threat of what the employer would have to work without or try to replace.)
What an employer would have once considered a better alternative – such as another equal offer for $120,000 – loses its appeal in light of the truth (sales pitch) of the $140,000 offer. If they are no longer equal in the mind of the employer, he or she must consciously decide if the other candidate at the lower price is still a better alternative. While there is no guarantee that the employer will prefer to pay more, the process of selling pushes the employer to the choice based on the true distinctions in the qualities of the candidates.
[1] Roger Fisher, William Ury and Bruce Patton, Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In. Gerald B. Wetlaufer, The Rhetorics of Negotiation (posted to SSRI).
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Negotiation Rhythms #2: Best Alternative to Negotiated Agreement
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
We know we want to push beyond our limits to capture as much value as possible in a negotiation. But how do we define those limits? It takes a five-word phrase to bring this concept into focus: Best Alternative to Negotiated Agreement (“BATNA”).
The BATNA for a car buyer might be the same car at a nearby dealership for $20,000. The BATNA for a home seller might be an offer from another party for $1 million. The BATNA for a child trading baseball cards might be to hold onto his favorite cards and enjoy looking at them rather than to trade them away.
Any agreement below (or, for a maximum limit, above) a BATNA would leave the negotiator worse off than in the absence of that particular agreement. Said another way, the negotiator would be better off with some other option – their BATNA – than accepting an agreement on those terms.
To properly identify a BATNA, we must do a lot of calculating, daydreaming, and going out in the world to test alternatives. But this creative process is necessary. When we believe that the only alternative is the one at hand, our negotiation position is dangerously weak. It is also dangerously ineffective because it leads to an arrangement that does not, in fact, make the negotiator better off than without it. And any deal that is not in both parties’ best interests is unstable and likely to collapse after it is made.
Countless factors go into naming and ranking one’s alternatives to arrive at a BATNA, and even then it is impossible to do so clearly as those factors cannot all be outlined in numerical format. A better offer might be less certain of being completed, so it might be more advantageous to make an agreement on less favorable terms today. For example, the other job offer might not be certain even though it appears it would be more advantageous if it were finalized. This is the old saying that a bird in the hand is better than two in the bush, and this can be dangerous for those who optimistically negotiate as if their imaginary alternatives are already in the hand. In the other extreme, this is very limiting for those who are very fearful of uncertainty, as they will accept disadvantageous terms for the simple purpose of having certain terms when a bit of risk in pursuit of a better alternative could have led to greater results.
Timing is important in other ways as well, as a negotiator with more time to come to an agreement will have more chances to find alternatives to the agreement at hand. "Wait and see" becomes a BATNA in itself. The opposite of this would be a party who must have resolution today, which would, of course, limit the alternatives.
Beyond hard limits on time, some people do not enjoy the back and forth process of negotiating. They might prefer to take this deal, and even to accept much less of the middle than is possible to capture, than to continue to seek alternatives or negotiate deals. For these people, the process itself inhibits the growth of BATNAs.
We’ll see in the next post – Negotiation Rhythms #3: Sales & Threats – how brainstorming or eliminating BATNAs changes the ZOPA and improves or weakens our force in negotiation.
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Negotiation Rhythms #1: Zone of Possible Agreement
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Each party will enter a negotiation with the knowledge of their limits and the desire to make as favorable a deal as possible.
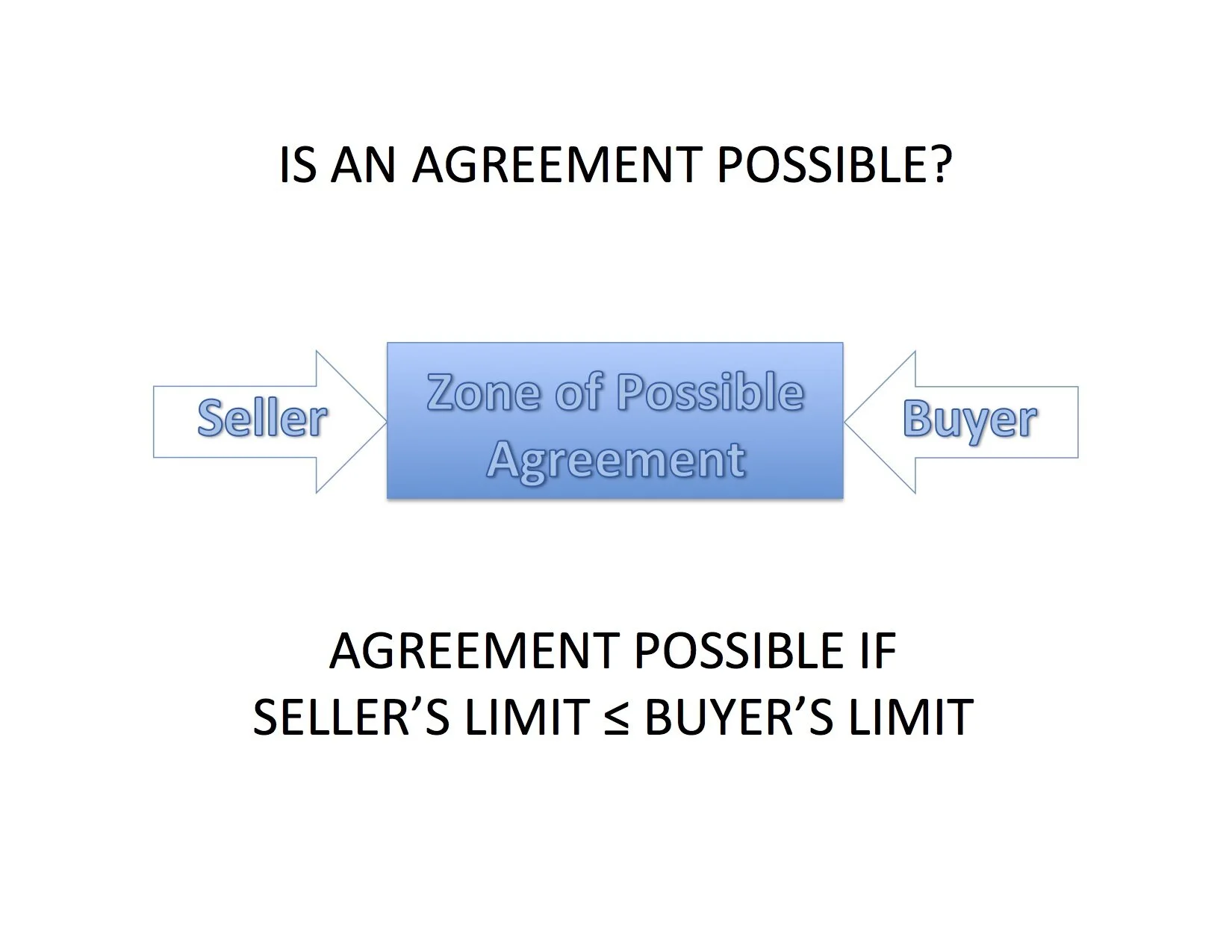
We begin our illustration of the basic negotiation rhythms with the fundamental negotiation question from Harvard Negotiation Project’s classic Getting to Yes[1]: Is there a Zone of Possible Agreement (“ZOPA”) between the limits set by each party?
An agreement is possible if the seller's limit is lower than the buyer's limit. Here's an example:
If an engineer is willing to work for a salary of $100K and a company recruiting that engineer is willing to pay $120K, there would be a ZOPA between $100K and $120K.
However, there would be no ZOPA if the amounts were reversed and the company would not offer more than $100K and the engineer would not accept less than $120K.
Capturing the ZOPA
Presuming that there is a ZOPA, the seller will want to sell for as much over the seller’s minimum as possible, and the buyer will want to buy for as much below the buyer’s maximum as possible.
It would be best for the seller to settle on a price at buyer’s maximum and for buyer to settle on a price at seller’s minimum.
Each is free to try to capture as much of the amount within the ZOPA as possible, especially if they do not know one another’s limits.
Hiding the ZOPA
The danger comes when one or more parties push so hard to settle on an agreement well above their minimum or below their maximum that they fail to discover that there is a ZOPA between the parties.
For example, the engineer would be at an advantage in the first example above if she convinced the company that she would not accept a salary below $120K. By pushing for $120K, she might end up with the maximum possible salary available from the company. However, she would end up with no deal at all – and have missed the chance to make a desirable agreement at somewhere between $100K and $120K – if she convinced the company she would take no less than $125K.
The opposite is also true. If the company convinced the engineer that they could offer no more than $95K, they would have convinced the engineer that there was no ZOPA and killed the deal.
ZOPA Conclusion
Each party has two conflicting goals in a negotiation:
1. Transparency: To discover a possible point of agreement, if one exists. This requires each party to be transparent enough about their limits that the parties can identify whether there is a ZOPA. If the parties kill the deal, they will have sacrificed the value of a beneficial agreement.
2. Ambiguity: To settle on a price that is as close to the other party’s limit as possible. This requires each party to be ambiguous in communicating their limits to encourage the opposing party to believe the ZOPA and their potential gain are smaller than they actually are. If a party settles at their limit, they will have sacrificed the benefit they could have captured by pushing to settle closer to the other party's limit.
Our next post, #2: Best Alternatives to Negotiated Agreement, illustrates how negotiators set their limits. Post #3: Sales & Threats shows the flexibility of the pattern by illustrating how negotiators use sales techniques to change the other party’s limit.
[1] Roger Fisher, William Ury and Bruce Patton, Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In.
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
Negotiation Rhythms
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
We’ve all heard plenty of advice about negotiating.
The business world directs us to stay rationally focused, rely on exhaustive preparation, think through alternatives, spend less time talking and more time listening and asking questions, and let the other side make the first offer.[1]
The psych world counsels us to listen first, sit down, find common ground, move in, keep cool, be brief, forget neutrality, avoid empty threats, and don’t yield.[2]
These tips don’t have much meaning without knowing the underlying principles of negotiations, and studying tips alone is about as meaningful as learning dance steps without ever hearing the music.
The following three-part series presents the rhythm of negotiations as described in the Harvard Negotiation Project’s Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In.[3] It should be useful for those first learning to hear this rhythm and for those who have been dancing since the bazaars of their youth who may need to go back to basics to learn some tricky new steps.
Read on!
#1: Zone of Possible Agreement
#2: Best Alternatives to Negotiated Agreement
#3: Sales & Threats
Attorney Mary Russell counsels individuals on startup equity, including:
You are welcome to contact her at (650) 326-3412 or at info@stockoptioncounsel.com.
[1] Take It Or Leave It: The Only Guide to Negotiating You Will Ever Need http://www.inc.com/magazine/20030801/negotiation.html via @Inc
[2] The Art of Negotiation | Psychology Today http://www.psychologytoday.com/articles/200701/the-art-negotiation
[3] Roger Fisher, William Ury and Bruce Patton, Getting to Yes: Negotiating Agreement Without Giving In.